Treatment of Leakages of Oxygen Pipeline Check Valve Flanges
Formulating a treatment plan
Oxygen pipeline maintenance hot work is the hot work with the highest risk in Steel. Oxygen has good combustion-supporting properties. There should be careful consideration about formulating plans when hot work occurs. Any carelessness may cause major accidents. The company attached great importance to it, and organized relevant experts and personnel from the oxygen plant to discuss and formulate an emergency repair plan.
1. Stopping oxygen supply
The company's manager first coordinates the use of oxygen, and the relevant users formulate a plan to reduce or stop using oxygen. The amount of reduction must be equal to or greater than the amount of oxygen sent by the branch pipeline, which is about 29500m3/h. Then through the scheduling confirmation of the oxygen plant, stop the oxygen compressor of 1#23 500m3/h unit and the oxygen piston of 6000m3/h unit.
2. Pressure relief of pipelines
Since the oxygen compressors of the two sets of units are equipped with check valves, the pressure of oxygen in this section of the pipeline can only be relieved by disassembling the valve flange after the gas is stopped. However, it is difficult to control the pressure relief speed after disassembling the flange. There is a certain risk, and high-pressure oxygen blowing through the valve flange is likely to damage the original flange gasket. To replace a large flange gasket, it is necessary to remove the old gasket that may remain, or even dismantle the entire valve, which greatly increases the repair time. By studying the drawings and checking the pipeline on site, it is determined to release the pressure through the nitrogen pressure relief port. Close the check valve, the 3 oxygen valves leading to the spherical tank——Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6. In order to ensure that the pressure difference on both sides of the valve is less than or equal to 0.3M Pa, first open the medium-pressure nitrogen to increase the pressure of the nitrogen pipeline where the ball nitrogen 7 is located and increase the pressure to greater than or equal to the oxygen pressure in the pipeline; open the ball nitrogen 7 valve. Then open the nitrogen release valve and release the oxygen pressure in the oxygen pipeline through the nitrogen release valve.
3. The replacement of nitrogen purge
After the pressure relief is completed, disassemble the flanges in front of the three valves of Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6. Slowly remove flanges, because there may be residual air in the stub after the leaked check valve. Add blind plates to the three oxygen parallel valves, but do not tighten the bolts to prevent accidents caused by leakages of oxygen from the side of the spherical tank due to the valve not being closed well. When disassembling the three valve flanges, it is also necessary to prevent any of the three valves from leaking. If there is air leakage from the disassembled flange and it has existed for a long time, it is necessary to consider that the air leakage of the three oxygen parallel valves is not closed well, and further measures should be taken.
Use the l#23 500m3/h oxygen permeable security nitrogen valve to send 0.1M Pa nitrogen to replace the oxygen in the pipeline, and release it through the leak at the flange where the oxygen 4, oxygen 5, and oxygen 6 valves are disassembled. After the purging is completed, take samples for testing, and stop sending nitrogen after passing the test. After the nitrogen replacement is completed and the hot work is completed, the construction party will be notified of the construction. Test at least once every 2 hours during the construction period to ensure that the oxygen content at the construction site does not exceed the standard.
4. The repair process
On the morning of September 22, the emergency repair plan was implemented. Make preparations in advance, and the relevant personnel are on standby on the spot, waiting for the dispatch notice. At 7:30, the company's relevant oxygen units began to gradually reduce oxygen consumption.
Oxygen pipeline maintenance hot work is the hot work with the highest risk in Steel. Oxygen has good combustion-supporting properties. There should be careful consideration about formulating plans when hot work occurs. Any carelessness may cause major accidents. The company attached great importance to it, and organized relevant experts and personnel from the oxygen plant to discuss and formulate an emergency repair plan.
1. Stopping oxygen supply
The company's manager first coordinates the use of oxygen, and the relevant users formulate a plan to reduce or stop using oxygen. The amount of reduction must be equal to or greater than the amount of oxygen sent by the branch pipeline, which is about 29500m3/h. Then through the scheduling confirmation of the oxygen plant, stop the oxygen compressor of 1#23 500m3/h unit and the oxygen piston of 6000m3/h unit.
2. Pressure relief of pipelines
Since the oxygen compressors of the two sets of units are equipped with check valves, the pressure of oxygen in this section of the pipeline can only be relieved by disassembling the valve flange after the gas is stopped. However, it is difficult to control the pressure relief speed after disassembling the flange. There is a certain risk, and high-pressure oxygen blowing through the valve flange is likely to damage the original flange gasket. To replace a large flange gasket, it is necessary to remove the old gasket that may remain, or even dismantle the entire valve, which greatly increases the repair time. By studying the drawings and checking the pipeline on site, it is determined to release the pressure through the nitrogen pressure relief port. Close the check valve, the 3 oxygen valves leading to the spherical tank——Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6. In order to ensure that the pressure difference on both sides of the valve is less than or equal to 0.3M Pa, first open the medium-pressure nitrogen to increase the pressure of the nitrogen pipeline where the ball nitrogen 7 is located and increase the pressure to greater than or equal to the oxygen pressure in the pipeline; open the ball nitrogen 7 valve. Then open the nitrogen release valve and release the oxygen pressure in the oxygen pipeline through the nitrogen release valve.
3. The replacement of nitrogen purge
After the pressure relief is completed, disassemble the flanges in front of the three valves of Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6. Slowly remove flanges, because there may be residual air in the stub after the leaked check valve. Add blind plates to the three oxygen parallel valves, but do not tighten the bolts to prevent accidents caused by leakages of oxygen from the side of the spherical tank due to the valve not being closed well. When disassembling the three valve flanges, it is also necessary to prevent any of the three valves from leaking. If there is air leakage from the disassembled flange and it has existed for a long time, it is necessary to consider that the air leakage of the three oxygen parallel valves is not closed well, and further measures should be taken.
Use the l#23 500m3/h oxygen permeable security nitrogen valve to send 0.1M Pa nitrogen to replace the oxygen in the pipeline, and release it through the leak at the flange where the oxygen 4, oxygen 5, and oxygen 6 valves are disassembled. After the purging is completed, take samples for testing, and stop sending nitrogen after passing the test. After the nitrogen replacement is completed and the hot work is completed, the construction party will be notified of the construction. Test at least once every 2 hours during the construction period to ensure that the oxygen content at the construction site does not exceed the standard.
4. The repair process
On the morning of September 22, the emergency repair plan was implemented. Make preparations in advance, and the relevant personnel are on standby on the spot, waiting for the dispatch notice. At 7:30, the company's relevant oxygen units began to gradually reduce oxygen consumption.
(1) Stopping oxygen supply
At 8:05, the amount of external oxygen consumption decreased significantly, and the oxygen generation dispatcher notified to stop the oxygen compressor of l#23 500m3/h unit. At 8:10am, stop the oxygen piston of the 6 000m3/h unit. Since the amount of nitrogen used externally has not been reduced, the two sets of air separation plants remain in operation.
(2) The pressure relief of the pipeline
At 8:12am, after closing the leaked check valve, the three oxygen valves leading to the spherical tank are Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5 and Oxygen 6. The three valves are in the normally open state for a long time, and are hardly opened or closed. An F-shaped wrench with 3 meters was made by welding with a pipe of DN65 in advance. It took more than half an hour to close the three valves. At 8:50am, open medium-pressure nitrogen (about 2.0M Pa) to pressurize the pipeline where the nitrogen ball 7 is located. After the pressure is balanced, open the nitrogen ball 7 valve; open the nitrogen release valve, and release the oxygen pressure in the oxygen pipe. At 9:20am, disassemble the flanges on the side of the check valves of Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6, and release the residual air behind the check valves. It takes a long time to deflate through the flange. It is suspected that the three oxygen parallel valves are not closed well. After tightening with an F-shaped wrench, there will be no more air leakage.
(3) The replacement of nitrogen purge
Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6 flange bolts are removed and a blind plate is provided in front of the valve to prevent the valve from not being closed well and leaking oxygen during construction, causing accidents. At 9:55am, the oxygen compressor of the l#23 500m3/h unit sends nitrogen to the oxygen pipeline for nitrogen purge, and releases through the three valve flange disassembly ports and the nitrogen release port. After purging for about 10 minutes, stop oxygen permeation after sampling and testing the oxygen content; stop nitrogen purging and replacement, and notify the construction personnel to start construction.
(4) Construction
Anyang Iron and Steel Engineering Technology Co., Ltd. with construction qualifications was hired to carry out the construction. Construction started at 10:15am, and the flange of the check valve was cut at 13:35pm, and the beveling began. Cotton yarn blocked the mouth. In order to prevent metal shavings from entering the pipe when beveling, plug the pipes on both sides with cotton yarn. At 17:30pm, lay the bevel, clean and degrease the bevel and the inner side of the pipes on both sides with trichlorethylene. At 17:45pm, the new flange was degreased and put in place, and started welding with argon arc welding. At 20:10pm, the welding seam was completed, and was tested for penetration. At 20:30pm, the construction was all over, and the construction workers were evacuated from the site.
(5) Purge
Open the l#23500m3/h oxygen compressor to pressurize nitrogen to purge the oxygen pipeline, and release it through the dismantling port of the three valve flanges and the nitrogen release port. The purpose is to prevent welding slag and cuttings from remaining in the pipeline and causing danger due to being contact with oxygen and frictional heat generation. Stop the oxygen compressor after purging for 20 minutes.
(6) Testing leakages
Take out the blind plates of the three valves of Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6, and restore them to their original state. Open the ball nitrogen 7 valve; pressurize the check valve flange and the three oxygen parallel valve flanges in stages with medium pressure nitrogen; test the leak with fat-free soapy water; the pressure test reaches the maximum pressure of the medium pressure nitrogen, and no leaks are found.
(7) Air supply
After passing the leakage test, close the ball nitrogen 7 valve. Close the nitrogen booster valve, and release the pressure. At 21:15pm, open the 6000m3/h oxygen piston and l#23500m3/h oxygen compressor to deliver oxygen. When the pressure reaches the pressure difference between the front and back of the valve within 0.3MPa, open oxygen 4, oxygen 5, and oxygen 6. An oxygen valve is used to send oxygen into the spherical tank and the pipeline to restore the user's use.
5. Causes and Analysis of Accidents
The pipeline with cracks and leaks has been in operation for more than 11 years, and the wall thickness of the weak point is measured every 5 years, but there is no comprehensive inspection for flaw detection of welding seams and pipelines. Through the observation and analysis of the cracks, it is found that the cracks are not completely cracks at welding seams (Figure 2), but part of them are cracks in the pipeline near the weld seam. This may be related to the initial welding condition of the joint. Improper welding caused excessive mechanical stress; coupled with the unnatural piping, the pipeline has been working for a long time under the medium pressure load of 1.5 to 2.5MPa, and the repeated working pressure changes result in stress concentration and leakage due to fatigue damage, slowly extending until the development of cracks. The emergency repair treatment took 13 hours, calculated as 60m3 of oxygen consumption for 1 ton of steel:
13× (6000+23500) ÷60=6391.7t
The accident caused Anyang Iron and Steel Company to reduce steelmaking by 6391.7 tons, which is not a small economic loss under the situation of severe steel efficiency.
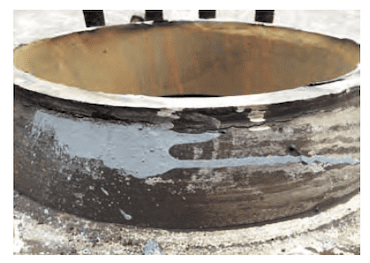
Figure 2 Cracks in the flange pipe of the check valve
6. Conclusion
Although the emergency repair was successful, the accident also sounded the alarm for us. The oxygen plant still has pipelines that were built earlier than this one. In the future, it is necessary to use the opportunity of maintenance to investigate gradually and comprehensively to prevent the recurrence of such accidents. The failure of the welding seam has its chance. However, this also requires us to strictly supervise the process pipelines, especially the pipelines that have almost no chance of maintenance after completion. Take adequate film inspections of the weld seams, and check them one by one to avoid hidden dangers for future use. In the maintenance process, due to the closure of some pipelines, the oxygen connection between the old and new system users was interrupted, and the oxygen pressure on both sides was unbalanced. The pressure of the new system was high, and that of the old system was low. It is planned to add another section of the pipeline to increase the connection path between the old and new systems and ensure the oxygen production of users during maintenance.
(2) The pressure relief of the pipeline
At 8:12am, after closing the leaked check valve, the three oxygen valves leading to the spherical tank are Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5 and Oxygen 6. The three valves are in the normally open state for a long time, and are hardly opened or closed. An F-shaped wrench with 3 meters was made by welding with a pipe of DN65 in advance. It took more than half an hour to close the three valves. At 8:50am, open medium-pressure nitrogen (about 2.0M Pa) to pressurize the pipeline where the nitrogen ball 7 is located. After the pressure is balanced, open the nitrogen ball 7 valve; open the nitrogen release valve, and release the oxygen pressure in the oxygen pipe. At 9:20am, disassemble the flanges on the side of the check valves of Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6, and release the residual air behind the check valves. It takes a long time to deflate through the flange. It is suspected that the three oxygen parallel valves are not closed well. After tightening with an F-shaped wrench, there will be no more air leakage.
(3) The replacement of nitrogen purge
Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6 flange bolts are removed and a blind plate is provided in front of the valve to prevent the valve from not being closed well and leaking oxygen during construction, causing accidents. At 9:55am, the oxygen compressor of the l#23 500m3/h unit sends nitrogen to the oxygen pipeline for nitrogen purge, and releases through the three valve flange disassembly ports and the nitrogen release port. After purging for about 10 minutes, stop oxygen permeation after sampling and testing the oxygen content; stop nitrogen purging and replacement, and notify the construction personnel to start construction.
(4) Construction
Anyang Iron and Steel Engineering Technology Co., Ltd. with construction qualifications was hired to carry out the construction. Construction started at 10:15am, and the flange of the check valve was cut at 13:35pm, and the beveling began. Cotton yarn blocked the mouth. In order to prevent metal shavings from entering the pipe when beveling, plug the pipes on both sides with cotton yarn. At 17:30pm, lay the bevel, clean and degrease the bevel and the inner side of the pipes on both sides with trichlorethylene. At 17:45pm, the new flange was degreased and put in place, and started welding with argon arc welding. At 20:10pm, the welding seam was completed, and was tested for penetration. At 20:30pm, the construction was all over, and the construction workers were evacuated from the site.
(5) Purge
Open the l#23500m3/h oxygen compressor to pressurize nitrogen to purge the oxygen pipeline, and release it through the dismantling port of the three valve flanges and the nitrogen release port. The purpose is to prevent welding slag and cuttings from remaining in the pipeline and causing danger due to being contact with oxygen and frictional heat generation. Stop the oxygen compressor after purging for 20 minutes.
(6) Testing leakages
Take out the blind plates of the three valves of Oxygen 4, Oxygen 5, and Oxygen 6, and restore them to their original state. Open the ball nitrogen 7 valve; pressurize the check valve flange and the three oxygen parallel valve flanges in stages with medium pressure nitrogen; test the leak with fat-free soapy water; the pressure test reaches the maximum pressure of the medium pressure nitrogen, and no leaks are found.
(7) Air supply
After passing the leakage test, close the ball nitrogen 7 valve. Close the nitrogen booster valve, and release the pressure. At 21:15pm, open the 6000m3/h oxygen piston and l#23500m3/h oxygen compressor to deliver oxygen. When the pressure reaches the pressure difference between the front and back of the valve within 0.3MPa, open oxygen 4, oxygen 5, and oxygen 6. An oxygen valve is used to send oxygen into the spherical tank and the pipeline to restore the user's use.
5. Causes and Analysis of Accidents
The pipeline with cracks and leaks has been in operation for more than 11 years, and the wall thickness of the weak point is measured every 5 years, but there is no comprehensive inspection for flaw detection of welding seams and pipelines. Through the observation and analysis of the cracks, it is found that the cracks are not completely cracks at welding seams (Figure 2), but part of them are cracks in the pipeline near the weld seam. This may be related to the initial welding condition of the joint. Improper welding caused excessive mechanical stress; coupled with the unnatural piping, the pipeline has been working for a long time under the medium pressure load of 1.5 to 2.5MPa, and the repeated working pressure changes result in stress concentration and leakage due to fatigue damage, slowly extending until the development of cracks. The emergency repair treatment took 13 hours, calculated as 60m3 of oxygen consumption for 1 ton of steel:
13× (6000+23500) ÷60=6391.7t
The accident caused Anyang Iron and Steel Company to reduce steelmaking by 6391.7 tons, which is not a small economic loss under the situation of severe steel efficiency.

Figure 2 Cracks in the flange pipe of the check valve
6. Conclusion
Although the emergency repair was successful, the accident also sounded the alarm for us. The oxygen plant still has pipelines that were built earlier than this one. In the future, it is necessary to use the opportunity of maintenance to investigate gradually and comprehensively to prevent the recurrence of such accidents. The failure of the welding seam has its chance. However, this also requires us to strictly supervise the process pipelines, especially the pipelines that have almost no chance of maintenance after completion. Take adequate film inspections of the weld seams, and check them one by one to avoid hidden dangers for future use. In the maintenance process, due to the closure of some pipelines, the oxygen connection between the old and new system users was interrupted, and the oxygen pressure on both sides was unbalanced. The pressure of the new system was high, and that of the old system was low. It is planned to add another section of the pipeline to increase the connection path between the old and new systems and ensure the oxygen production of users during maintenance.
Related News
- Failure and Crack Analysis of an EO/EG Unit Tower Inlet Flange
- Pipe Flange Bolt Tightening in LNG Projects: Key Considerations
- Ultrasonic Testing of High-Neck Flange Welds
- Underwater Flange Connection Methods for Submarine Pipelines
- Key Technologies for Pressure Vessel Testing and Flange Connection Design
- Installation of Main Bolts for Lap Joint Flange in High-Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors
- Structural Design and Finite Element Analysis of Anchor Flanges
- Key Welding Technology for High-Neck Flange and Steel Pipe Joints
- The Design and Calculation of Stamped Lap Joint Flanges
- Development of Manufacturing Large Anchor Flanges
