Threaded Flanges at the End of Valve Bodies of High-pressure Oil & Gas Wellhead Devices
Abstract: The structure of the threaded flange at the end of the valve body of the high-pressure oil and gas wellhead device is introduced. The strength calculation method of this type of threaded flange and its common specifications and dimensions are given. The threaded flange is safe and reliable after strength testing. In view of the current diversity of design calculations of threaded flanges, it is believed that appropriate standards can be formulated to regulate the entire process of design, manufacturing and acceptance, ensuring product quality, and thereby improving the safe performance of wellhead equipment.
The end of high-pressure valves and pipelines generally are connected by integral flanges or welded flanges. Factors such as the weldability of the material, stress corrosion of the welding seam, heat treatment and non-destructive testing of the welding seam need to be considered due to the influence of the pressure, temperature and corrosion of the medium, which increases the manufacturing difficulty and cost, and the working conditions are also restricted. The application of welding flanges is greatly limited. It is ideal to use an integral flange, but its application is limited due to its high material cost and higher requirements for forging equipment and processing equipment. Commonly used threaded flanges are not used under high pressure and their applications are also limited.
To make up for the shortcomings in the application of integral flanges, welded flanges and commonly used threaded flanges, and at the same time achieve better performance, it is more reasonable to develop and apply threaded flanges at the end of the valve body of high-pressure oil and gas wellhead devices. The structural design and strength calculation of the threaded flange at the end of the valve body of the high-pressure oil and gas wellhead device will be introduced based on many years of design and use experience at home and abroad, providing a reference for relevant departments and manufacturers of oil and gas fields.
Brief structure analysis
The structure of the threaded flange at the end of the valve body of high-pressure oil and gas wellhead devices widely used in oil and gas fields in China is shown in Figure 1. The pressure ratings are 21, 25, 35, and 60.70MPa. The diameter is mainly 65mm.
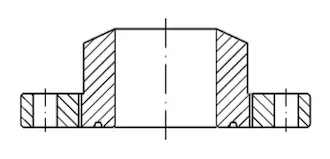
Figure 1 The structure of threaded flanges at the end of the high-pressure oil and gas well valve body
As can be seen from Figure 1, the valve body and flange are connected through threads. The threads are outside the BX-type sealing groove. The flange does not contact the medium in the valve body. The material selection of the valve body and flange can be different, so the material and manufacturing cost of the threaded flange at the end of the valve body is low, and the processing technology is good. The same type of structure is a high-pressure lens pad threaded flange, as shown in Figure 2. This kind of threaded flange is widely used in China's petroleum and chemical industries, such as ammonia synthesis units, ethylene synthesis and urea synthesis units. It is mainly used for connecting high-pressure valves and high-pressure pipelines. The medium’s pressure is high. The maximum pressure is up to 250MPa; the temperature is high and corrosiveness is strong, especially the high-frequency vibration caused by high-pressure air flow fluctuations during operation is far worse than that in oil and gas fields. Common standards include JB/T1308.2-1999 and JB2768-1992.
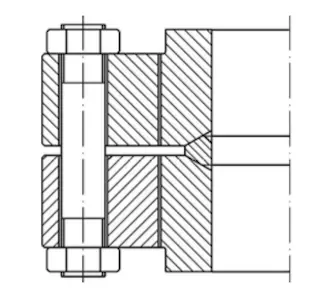
Figure 2 Common structures of threaded flanges for high-pressure lens pads
Calculating strength
The threaded flange at the end of the wellhead device valve body and the commonly used threaded flange have different stress conditions due to the different relative positions of the thread and the sealing surface; at the same time, it is also different from the integral flange and the welded flange, so its math model for strength calculation is different from them.
A strength calculation method for the threaded flange at the end of the wellhead device valve body is provided through step-by-step analysis.
The end of high-pressure valves and pipelines generally are connected by integral flanges or welded flanges. Factors such as the weldability of the material, stress corrosion of the welding seam, heat treatment and non-destructive testing of the welding seam need to be considered due to the influence of the pressure, temperature and corrosion of the medium, which increases the manufacturing difficulty and cost, and the working conditions are also restricted. The application of welding flanges is greatly limited. It is ideal to use an integral flange, but its application is limited due to its high material cost and higher requirements for forging equipment and processing equipment. Commonly used threaded flanges are not used under high pressure and their applications are also limited.
To make up for the shortcomings in the application of integral flanges, welded flanges and commonly used threaded flanges, and at the same time achieve better performance, it is more reasonable to develop and apply threaded flanges at the end of the valve body of high-pressure oil and gas wellhead devices. The structural design and strength calculation of the threaded flange at the end of the valve body of the high-pressure oil and gas wellhead device will be introduced based on many years of design and use experience at home and abroad, providing a reference for relevant departments and manufacturers of oil and gas fields.
Brief structure analysis
The structure of the threaded flange at the end of the valve body of high-pressure oil and gas wellhead devices widely used in oil and gas fields in China is shown in Figure 1. The pressure ratings are 21, 25, 35, and 60.70MPa. The diameter is mainly 65mm.

Figure 1 The structure of threaded flanges at the end of the high-pressure oil and gas well valve body
As can be seen from Figure 1, the valve body and flange are connected through threads. The threads are outside the BX-type sealing groove. The flange does not contact the medium in the valve body. The material selection of the valve body and flange can be different, so the material and manufacturing cost of the threaded flange at the end of the valve body is low, and the processing technology is good. The same type of structure is a high-pressure lens pad threaded flange, as shown in Figure 2. This kind of threaded flange is widely used in China's petroleum and chemical industries, such as ammonia synthesis units, ethylene synthesis and urea synthesis units. It is mainly used for connecting high-pressure valves and high-pressure pipelines. The medium’s pressure is high. The maximum pressure is up to 250MPa; the temperature is high and corrosiveness is strong, especially the high-frequency vibration caused by high-pressure air flow fluctuations during operation is far worse than that in oil and gas fields. Common standards include JB/T1308.2-1999 and JB2768-1992.

Figure 2 Common structures of threaded flanges for high-pressure lens pads
Calculating strength
The threaded flange at the end of the wellhead device valve body and the commonly used threaded flange have different stress conditions due to the different relative positions of the thread and the sealing surface; at the same time, it is also different from the integral flange and the welded flange, so its math model for strength calculation is different from them.
A strength calculation method for the threaded flange at the end of the wellhead device valve body is provided through step-by-step analysis.
(1) When the threaded flange at the end of the valve body of the wellhead device is designed using the WATERS method, important strength indicators such as bending, shearing, and extrusion of the connecting thread are not calculated, which is not suitable.
(2) The Ministry of Chemical Industry of China organized scientific research institutes to conduct special research on the high-pressure threaded flange of the lens pad, and adopted internationally advanced design methods and standards, such as the German AD specifications and the former Soviet Union TY8100 standard) to conduct special research on important strength indicators such as thread bending, shearing and extrusion of the threaded flange were calculated, and a standard design method was formed, which is "Design and Calculation of High-Pressure Threaded Flanges of Lens Pad" in HG20582-1998 "Regulations on Strength Calculation of Steel Chemical Containers". Years of use in domestic chemical engineering have proven that using this method to design and calculate the high-pressure threaded flange of the lens pad is appropriate, safe and reliable.
(3) Although the threaded flange at the end of the wellhead device valve body and the threaded flange of the high-pressure lens gasket have different gasket forms, the former is a BX gasket and the latter is a lens gasket. According to references, it can be seen that the sealing mechanism of the two is consistent. They are both radial pressure self-tightening seals. Their stress conditions are the same. Therefore, they belong to the same flange type and the same strength calculation method can be used, which is "Design and Calculation of High-pressure Threaded Flanges for Lens Gaskets" in HG20582-1998 "Strength Calculation of Steel Chemical Containers". The minimum load required by the bolt in the pre-tightened state is calculated based on the characteristics of the BX gasket, and then the load is substituted into the strength calculation formula of high-pressure threaded flanges of lens gaskets for calculation.
(4) The flange connection size is determined based on the usage of wellheads in domestic oil and gas fields based on the API 6A standard. The pressure levels are 21, 35, and 70MPa; the diameter specifications are 46, 52, and 65mm; the allowable stress of bolts is greater than and equal to 362MPa, and the flange connection dimensions, namely the bolt center circle size, flange outer diameter, bolt specification and quantity, are the same API 6A integral flange size; the gasket ring should be API 6A BX type gasket ring of the same specification according to the diameter; the flange thickness and connecting thread should be determined according to the calculation results.
The specifications and dimensions of the threaded flange at the end of the valve body of several commonly used wellhead devices are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Specifications and dimensions of the threaded flange at the end of the valve body of commonly used wellhead devices
| Nominal pressure/MPa | Nominal diameters/ mm |
Outer diameters of flanges/ mm |
Total flange thickness/mm | Distribution diameters of bolts/mm | Sizes | Bolt diameter /mm | Numbers of bolts | Types of gaskets |
| 70 | 46 | 190 | 42 | 146 | M100 X 2 | 20 | 8 | BX151 |
| 70 | 52 | 200 | 44 | 159 | M 115 X 2 | 20 | 8 | BX152 |
| 70 | 65 | 232 | 51 | 184 | M 125 X 2 | 22 | 8 | BX153 |
| 35 | 65 | 245 | 49 | 190 | M125 X 2 | 24 | 8 | BX153* |
*Because the BX gasket has a reasonable force and is easier to tighten than the R-type gasket, the stress on the bolt is reduced and the flange structure is tight. The flange’s thickness and bolt’s specifications calculated using this specification are far smaller than those in Table 1. The data listed are small. However, to be consistent with the standard and actual well site dimensions, the dimensions in Table 1 were selected.
(5) Through calculation, it is believed that the threaded flanges at the end of the valve body of the above wellhead devices are safe and reliable.
Related News
- Low-Temperature Flange Sealing Solutions for Cryogenic Chemical Pipelines
- Innovative Technology for Automatic Alignment in Underwater Flange Assembly
- Stamped Steel Slip-On Flanges
- Design and Finite Element Analysis of Anchor Flanges for Oil & Gas Pipelines
- Forming and Manufacturing Technology of Anchor Flanges
- Structure and Materials of Anchor Flanges
- Flanges for Pressure Vessels
- An Introduction to Socket Welded Neck Flanges
- Heat Treatment & Mechanical Properties of ASTM A350 LF3 Flanges (Part Two)
- Heat Treatment & Mechanical Properties of ASTM A350 LF3 Flanges (Part One)
