How to identify and choose flange gaskets - part one
Flat gaskets used in the industry generally consist of a sealing element and an inner and outer reinforcing ring, which is a key part of the leakage prevention. Commonly used materials are non-metallic materials, such as flexible graphite, PTFE, fiber reinforced rubber-based composite panels. In addition, the sealing element material can also be rigid or flexible metal, typically used in applications where pressure and temperature are high.
A non-metallic sealing element is usually reinforced with metal materials, which also facilitates the manufacturing process of fragile materials like graphite. The reinforcing material may be a metal sheet or a wire mesh, of which, metal sheets are often punched to enhance the reinforcing effect and increase the elasticity, and then bonded together by an adhesive and rolling. The sealing element may also be provided with a surface layer or an anti-adhesive treatment layer to increase the sealing effect and prevent the flange sealing surface from sticking.
The outer reinforcing ring or outer ring materials are all solid metals, and their functions are as follows.
• Let the sealing element to be aligned during installation;
• Prevent damage to the sealing element from excessive compression, prevent gasket being blown and reduce flange rotation.
• The outer reinforcing ring is not in contact with the sealing medium and therefore does not require resistance to media corrosion and often made of carbon steel. The outer reinforcing ring can also be made integral with the sealing element, such as grooved metal gaskets, gaskets reinforced by the corrugated metal sheet.
• The inner reinforcing ring or inner ring is in contact with the fluid and its material should be resistant to corrosion from the sealing medium. The role of the inner reinforcement ring is to prevent gaps between the sealing element and the container or pipe flange to avoid this gap from interfering with the flow of fluid and the resulting fluid from impacting on the gasket.
Non-metallic flat gasket - PTFE coated gasket
The PTFE coated gasket is a non-metal composite soft gasket, generally consisting of two parts: the wrapper and the insert. The primary function of the wrapper is corrosion resistance and is typically made of PTFE material. The insert (filler) is non-metallic materials with or without metal reinforcement, usually made of asbestos rubber.
PTFE-coated gaskets are mainly suitable for raised face pipe flange and flat face steel flange connections, with corrosive media whose nominal pressure is between 0.6 MPa and 5.0 MPa, and working temperature between 0 °C and 150 °C, or media with high cleanliness requirements.
The PTFE-coated gaskets for pipe flanges can be divided into three types according to the manufacturing methods: slicing type, machining type, and folding type.
For machining type, the inner diameter of the coated layer can be consistent with that of the flange to prevent turbulence in the fluid at the flange. For the folding type gasket, it is a strip-shaped PTFE film with a thickness of 0.4-0.8 mm, which is heat-sealed and wrapped around the annular core material in a U shape. It is easy to manufacture and suitable for large flange seals.
Metal composite gasket - Metal spiral wound gasket
The metal spiral wound gasket is a semi-metal flat gasket which is spirally wound from a metal strip and a non-metal strip. Wound gaskets can be divided into four types according to their different structures: basic type, type with inner ring, type with locating ring, type with inner ring and locating ring.
Characteristics of metal spiral wound gaskets:
• Good compression property and resilience;
• Multiple seals and a certain self-tightening function;
• It is not sensitive to the defects of the flange sealing surface, and is easy to be aligned and disassembled;
• Alleviate the effects of pressure, temperature changes and mechanical vibrations;
• It can maintain its excellent sealing performance under various harsh conditions such as high temperature, low pressure, high vacuum, etc.
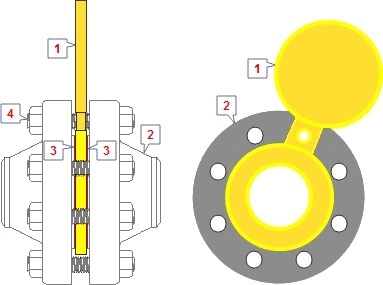
1. Spectacle blind 2. Flanges 3. Gaskets 4. Stud Bolts
A non-metallic sealing element is usually reinforced with metal materials, which also facilitates the manufacturing process of fragile materials like graphite. The reinforcing material may be a metal sheet or a wire mesh, of which, metal sheets are often punched to enhance the reinforcing effect and increase the elasticity, and then bonded together by an adhesive and rolling. The sealing element may also be provided with a surface layer or an anti-adhesive treatment layer to increase the sealing effect and prevent the flange sealing surface from sticking.
The outer reinforcing ring or outer ring materials are all solid metals, and their functions are as follows.
• Let the sealing element to be aligned during installation;
• Prevent damage to the sealing element from excessive compression, prevent gasket being blown and reduce flange rotation.
• The outer reinforcing ring is not in contact with the sealing medium and therefore does not require resistance to media corrosion and often made of carbon steel. The outer reinforcing ring can also be made integral with the sealing element, such as grooved metal gaskets, gaskets reinforced by the corrugated metal sheet.
• The inner reinforcing ring or inner ring is in contact with the fluid and its material should be resistant to corrosion from the sealing medium. The role of the inner reinforcement ring is to prevent gaps between the sealing element and the container or pipe flange to avoid this gap from interfering with the flow of fluid and the resulting fluid from impacting on the gasket.
Non-metallic flat gasket - PTFE coated gasket
The PTFE coated gasket is a non-metal composite soft gasket, generally consisting of two parts: the wrapper and the insert. The primary function of the wrapper is corrosion resistance and is typically made of PTFE material. The insert (filler) is non-metallic materials with or without metal reinforcement, usually made of asbestos rubber.
PTFE-coated gaskets are mainly suitable for raised face pipe flange and flat face steel flange connections, with corrosive media whose nominal pressure is between 0.6 MPa and 5.0 MPa, and working temperature between 0 °C and 150 °C, or media with high cleanliness requirements.
The PTFE-coated gaskets for pipe flanges can be divided into three types according to the manufacturing methods: slicing type, machining type, and folding type.
For machining type, the inner diameter of the coated layer can be consistent with that of the flange to prevent turbulence in the fluid at the flange. For the folding type gasket, it is a strip-shaped PTFE film with a thickness of 0.4-0.8 mm, which is heat-sealed and wrapped around the annular core material in a U shape. It is easy to manufacture and suitable for large flange seals.
Metal composite gasket - Metal spiral wound gasket
The metal spiral wound gasket is a semi-metal flat gasket which is spirally wound from a metal strip and a non-metal strip. Wound gaskets can be divided into four types according to their different structures: basic type, type with inner ring, type with locating ring, type with inner ring and locating ring.
Characteristics of metal spiral wound gaskets:
• Good compression property and resilience;
• Multiple seals and a certain self-tightening function;
• It is not sensitive to the defects of the flange sealing surface, and is easy to be aligned and disassembled;
• Alleviate the effects of pressure, temperature changes and mechanical vibrations;
• It can maintain its excellent sealing performance under various harsh conditions such as high temperature, low pressure, high vacuum, etc.

1. Spectacle blind 2. Flanges 3. Gaskets 4. Stud Bolts
Related News
- Installation of Main Bolts for Lap Joint Flange in High-Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors
- Structural Design and Finite Element Analysis of Anchor Flanges
- Key Welding Technology for High-Neck Flange and Steel Pipe Joints
- The Design and Calculation of Stamped Lap Joint Flanges
- Development of Manufacturing Large Anchor Flanges
- Hardfacing the Inner Surface of Long-Neck Flanges Using CO₂ Gas-Shielded Welding
- UHV High-Neck Flange Welding
- Application of High-Neck Flange to UHV Steel Pipe Tower
- Analysis of the Cracking Cause of High-Neck Flanges
- Anchor Flanges for the East-West Gas Transmission Project
