Application of TIG Welding to SS Slip-on Flanges (Part one)
Abstract: Stainless steel slip-on flange and pipe fittings are connected by TIG welding, and self-flux welding is adopted for the flange’s sealing surface. The non-sealing surface of the flange is welded with wire to realize the function of the connection of the flange.
1. Introduction
Tungsten argon arc welding (TIG) is a welding method that uses tungsten rods as electrodes and inert gases such as hydrogen and helium as protective gases. Refractory metals are used as electrodes, and the electrodes do not melt in the welding process. Therefore, the welding process is stable, the welding seam is formed well, and it is easy to obtain high-quality welding seams. It is suitable for manual welding of aluminum and its alloys, stainless steel, high-temperature alloys, titanium alloys and refractory active metals such as molybdenum, niobium and aluminum. Because the price of helium is much higher than that of argon, argon is mainly used as a protective gas in industry.
A flange is used to fix pipeline equipment and pipe fittings on a flange plate first and add flange gaskets between the two flange plates; fasten them together with bolts to complete the connection. A flange is easy to use and can withstand high pressure. It is an important connecting method for pipeline construction. TIG welding is the first choice for fixing stainless steel flanges and pipe fittings.
2. The selection of welding equipment
(1) Welding machines: choose tungsten argon arc welding machines, such as WSM series DC tungsten pulse argon arc welding machines, which have automatic functions of the current slow rise and current attenuation.
(2) Welding torches: commonly used welding torches are divided into water-cooled type and air-cooled type. The former is used for extensive current welding (greater than and equal to 150A), and the latter is used for small current welding (less than and equal to 150A).
3. The selection of welding materials
(1) Argon: It has an excellent protective effect. It neither chemically interacts with the metal nor dissolves in the metal, making the metallurgical reaction of the molten pool in the welding process simple and easy to control. Therefore, to obtain high-quality welding seams, the arc burns very stably in argon and still burns stably in the case of small current welding (less than 10A). It can weld active metals that are easy to oxidize and nitride, ferrous metals with high melting points, and dissimilar metals, which are widely used in aviation, atomic energy, petrochemical engineering, power plant boilers, machinery and other fields. To ensure the best welding quality, the purity of fluorine gas is usually required to reach more than 99.99%.
(2) Welding wire: The common types of argon welding wire are 304, 308, 308L, 3161, etc. The principle of selection is that the mechanical properties of the welding seam metal should be higher than or equal to the limit value specified by the base metal. When necessary, other properties should not be lower than the corresponding requirements of the base metal; or the mechanical properties and other properties should meet the technical requirements specified in the design documents.
(3) Tungsten electrode: Because pure tungsten is not easy to strike the arc, thoriated tungsten electrode or cerium tungsten electrode is generally used. The arc beam of the cerium tungsten electrode is slender; it has concentrated heat, long service life, and it is easy to start the arc. More importantly, the radiation hazard is much smaller than that of thoriated tungsten. Therefore, it is recommended to use the cerium tungsten electrode for gas tungsten-shielded welding. If the surface of the tungsten electrode is brown, yellow-green or blue, it means that the terminal is seriously oxidized and should be re-polished before use.
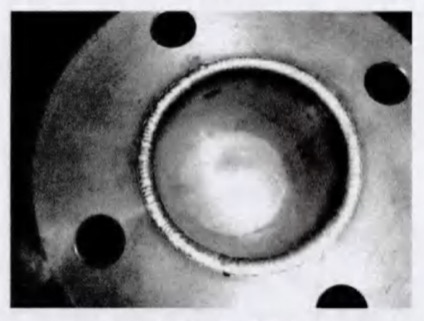
Figure 1 Welding of flanges and pipes

Figure 2 Position 1 before welding
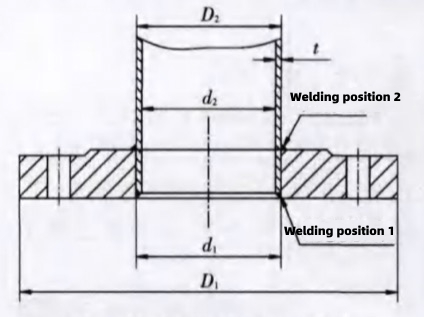
Figure 3 Position 1 after welding
1. Introduction
Tungsten argon arc welding (TIG) is a welding method that uses tungsten rods as electrodes and inert gases such as hydrogen and helium as protective gases. Refractory metals are used as electrodes, and the electrodes do not melt in the welding process. Therefore, the welding process is stable, the welding seam is formed well, and it is easy to obtain high-quality welding seams. It is suitable for manual welding of aluminum and its alloys, stainless steel, high-temperature alloys, titanium alloys and refractory active metals such as molybdenum, niobium and aluminum. Because the price of helium is much higher than that of argon, argon is mainly used as a protective gas in industry.
A flange is used to fix pipeline equipment and pipe fittings on a flange plate first and add flange gaskets between the two flange plates; fasten them together with bolts to complete the connection. A flange is easy to use and can withstand high pressure. It is an important connecting method for pipeline construction. TIG welding is the first choice for fixing stainless steel flanges and pipe fittings.
2. The selection of welding equipment
(1) Welding machines: choose tungsten argon arc welding machines, such as WSM series DC tungsten pulse argon arc welding machines, which have automatic functions of the current slow rise and current attenuation.
(2) Welding torches: commonly used welding torches are divided into water-cooled type and air-cooled type. The former is used for extensive current welding (greater than and equal to 150A), and the latter is used for small current welding (less than and equal to 150A).
3. The selection of welding materials
(1) Argon: It has an excellent protective effect. It neither chemically interacts with the metal nor dissolves in the metal, making the metallurgical reaction of the molten pool in the welding process simple and easy to control. Therefore, to obtain high-quality welding seams, the arc burns very stably in argon and still burns stably in the case of small current welding (less than 10A). It can weld active metals that are easy to oxidize and nitride, ferrous metals with high melting points, and dissimilar metals, which are widely used in aviation, atomic energy, petrochemical engineering, power plant boilers, machinery and other fields. To ensure the best welding quality, the purity of fluorine gas is usually required to reach more than 99.99%.
(2) Welding wire: The common types of argon welding wire are 304, 308, 308L, 3161, etc. The principle of selection is that the mechanical properties of the welding seam metal should be higher than or equal to the limit value specified by the base metal. When necessary, other properties should not be lower than the corresponding requirements of the base metal; or the mechanical properties and other properties should meet the technical requirements specified in the design documents.
(3) Tungsten electrode: Because pure tungsten is not easy to strike the arc, thoriated tungsten electrode or cerium tungsten electrode is generally used. The arc beam of the cerium tungsten electrode is slender; it has concentrated heat, long service life, and it is easy to start the arc. More importantly, the radiation hazard is much smaller than that of thoriated tungsten. Therefore, it is recommended to use the cerium tungsten electrode for gas tungsten-shielded welding. If the surface of the tungsten electrode is brown, yellow-green or blue, it means that the terminal is seriously oxidized and should be re-polished before use.

Figure 1 Welding of flanges and pipes

Figure 2 Position 1 before welding

Figure 3 Position 1 after welding
Related News
- Failure and Crack Analysis of an EO/EG Unit Tower Inlet Flange
- Pipe Flange Bolt Tightening in LNG Projects: Key Considerations
- Ultrasonic Testing of High-Neck Flange Welds
- Underwater Flange Connection Methods for Submarine Pipelines
- Key Technologies for Pressure Vessel Testing and Flange Connection Design
- Installation of Main Bolts for Lap Joint Flange in High-Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors
- Structural Design and Finite Element Analysis of Anchor Flanges
- Key Welding Technology for High-Neck Flange and Steel Pipe Joints
- The Design and Calculation of Stamped Lap Joint Flanges
- Development of Manufacturing Large Anchor Flanges
